The effects of Diabetes: how to lead a healthy life and mitigate its risks

According to the WHO, “diabetes causes serious diseases such as blindness, kidney failure, myocardial infarction, stroke and lower limb amputation”.
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects health and puts millions of people at risk around the world.
It arises when the body cannot adequately regulate blood glucose levels. There are two main types: type 1 diabetes, where the body does not produce insulin, and type 2 diabetes, where the body does not use insulin effectively. High blood sugar is the trigger that can lead to serious complications that can seriously affect health if not properly controlled.
Health Risks of Diabetes
High blood glucose levels can have negative effects on various organs and systems in our body, putting our survival at risk. Some of the most common risks include:
Cardiovascular problems: Diabetes increases the risk of heart disease and stroke.
Kidney damage: Excess sugar can affect the functioning of the kidneys, affecting essential functions of our body.
Vision problems: Diabetes can cause damage to the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to problems such as retinopathy.
Nerve damage: It can generate neuropathy, especially in the extremities, causing pain and loss of sensitivity, being also an extremely adverse and painful situation, which becomes the most devastating face of this disease.
Tips to adequately and safely maintain the sugar levels in our blood:
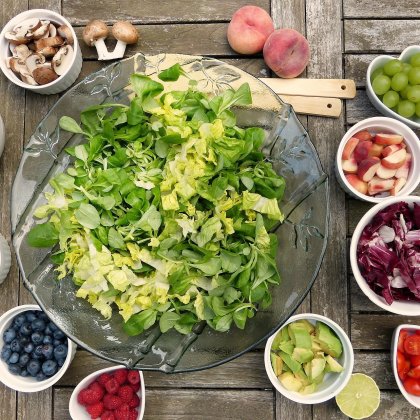
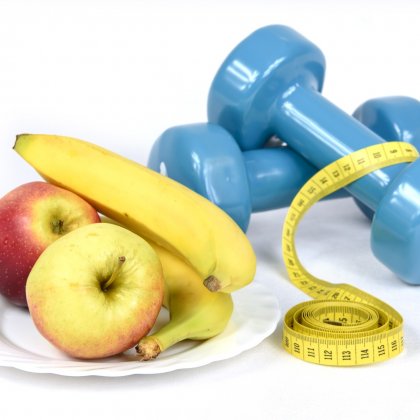
- Eat a healthy and balanced diet: Choose foods rich in fiber, proteins and healthy fats, and avoid sugary and processed products, which are transformed into glucose and put your health at risk.
- Exercise regularly: Exercise helps the body's cells to use glucose better and to reduce blood sugar levels, promoting proper oxygenation. It also improves your mood and reduces stress levels, have fun exercising!
- Portion control: Less is more, prefer to eat adequate and nutritious amounts to avoid excessive sugar levels. Give your body what it really needs.
- Sleep well and reduce stress: Good rest and stress management are key, as insomnia and chronic stress can raise blood sugar. Avoid smoking, its distortions and effects seriously affect health by damaging the vascular system and altering the proper metabolism of the body.
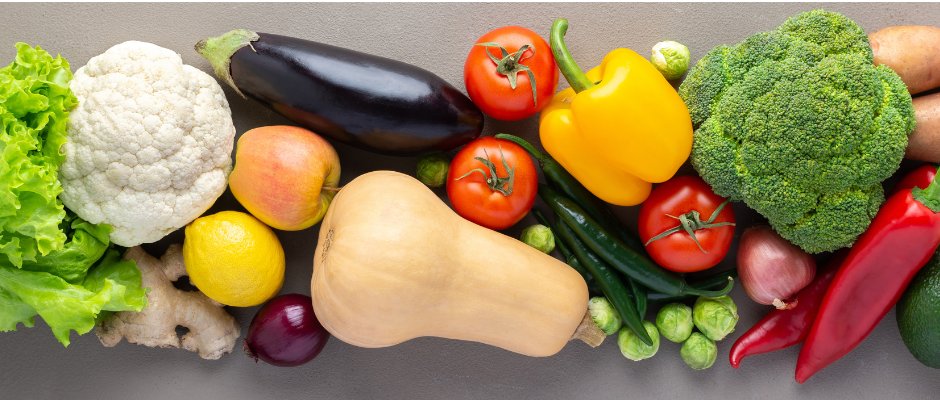
5. Cook Healthy Dishes to Control Diabetes. Having a proper diet is a fundamental ally for health.
Prefer low glycemic index foods: fresh vegetables, legumes, fruits such as apples and berries, and whole grains are ideal because they digest slowly and keep blood sugar stable. Enjoy your preparations!
Accompany your preparations with olive oil and avocado as they contain healthy fats that notably benefit the heart without raising blood sugar.